Supplements
BCAA Fruit Punch
BCAA Fruit Punch
Couldn't load pickup availability
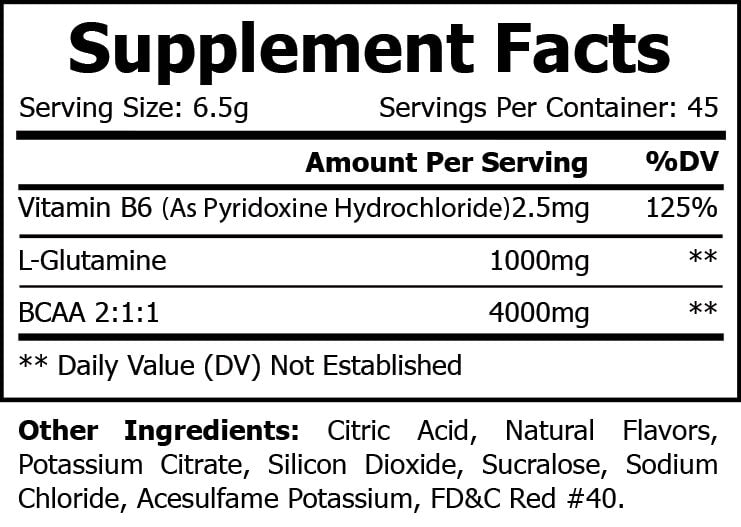
BCAA stands for Branched-chain amino acids: which prevent fatigue and improve concentration, reduce protein and muscle breakdown during and after an intense exercise. BCAA Post Workout after an intense workout has been shown to aid in maintaining muscle growth and energy required to reduce muscle breakdown. Containing: L-Glutamine for enhanced exercise performance, L-leucine for stimulated muscle growth, Vitamin B6 for energy and L-Valine for promoting muscle growth and tissue support.*
| Formula Purposes & Benefits |
|
BCAA Powder Fruit Punch is synthesized to improve exercise performance, increase muscle protein synthesis, prevent muscle tissue breakdown, support immunity, gut health, and recovery. Our product is synthesized utilizing the latest scientific research and formulated with optimal ratios of branch chain amino acids to produce world class results.
|
|
Formula Ingredient Deck |
Benefits Of Each Ingredient |
|
Vitamin B6 pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) |
|
|
BCAA 2:1 Ratio |
|
|
L-Glutamine |
|
| Proper Use of This Supplement |
|
Suggested Use: As a dietary supplement Mix 1/2 a scoop (6.5g) in 8 - 10 ounces of cold beverage. It will take a few minutes for all the powder to dissolve in the beverage. Best taken pre-workout, post-workout or between meals |
| Our Formula Vs Other Formulas on the Market. | |
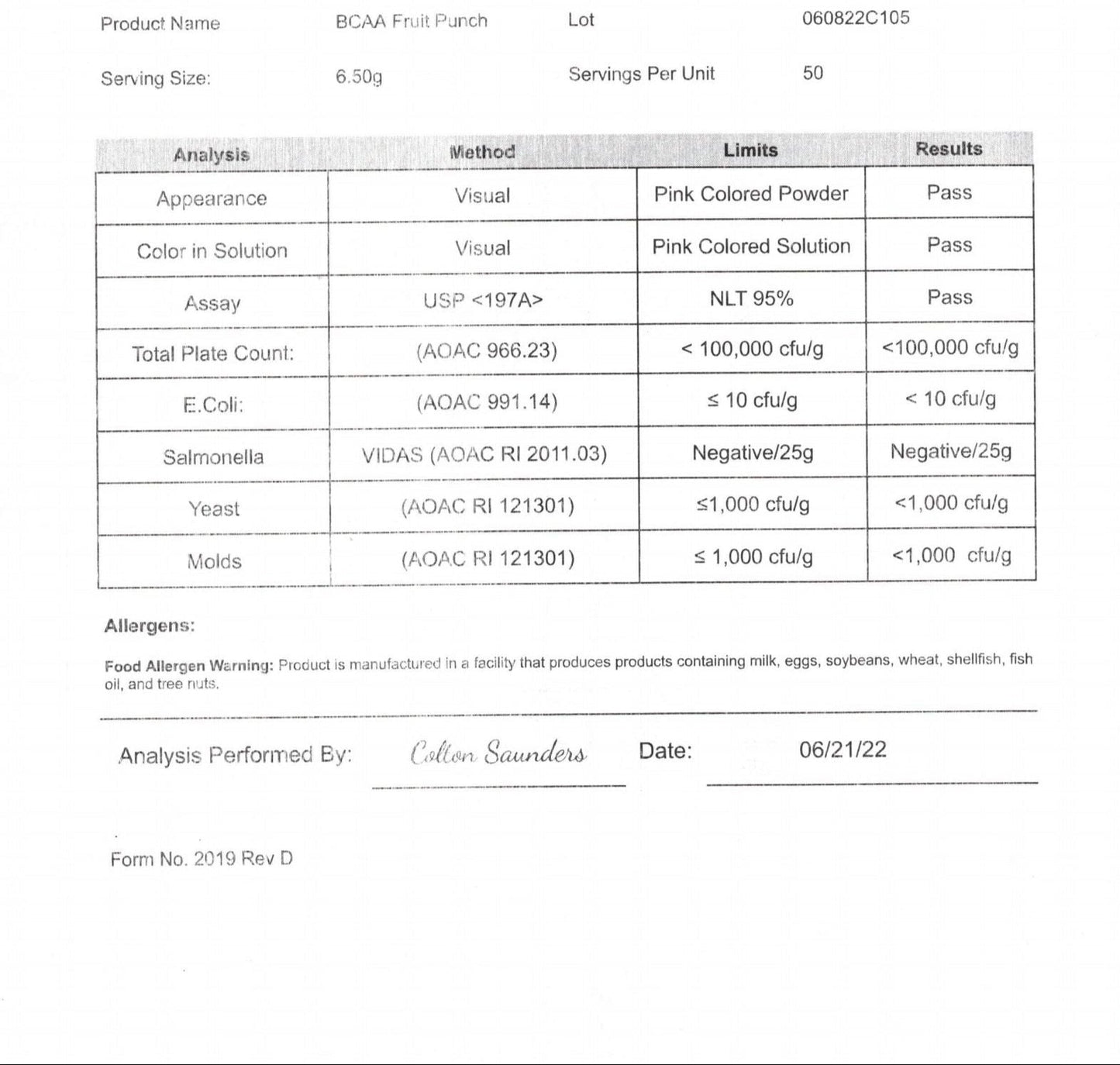
| 1. Uses third party independently tested ingredients that are made in the USA, GMP certified, and made in an FDA registered facility. | 1. Source cheap ingredients from heavily polluted soils. Even “organic” supplements not third party tested have been removed by FDA due to high levels of heavy metals. |
| 2. Utilizes efficacious evidence-based dosages with optimal ratios of amino acids to support exercise performance and recovery. | 2. Use low amounts of cheap forms of amino acids that result in poor absorption and muscle growth, recovery, and exercise performance. |
Sources:
- Cruzat, V., Macedo Rogero, M., Noel Keane, K., Curi, R., & Newsholme, P. (2018). Glutamine: Metabolism and Immune Function, Supplementation and Clinical Translation. Nutrients, 10(11), 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111564
- Ueland, P. M., McCann, A., Midttun, Ø., & Ulvik, A. (2017). Inflammation, vitamin B6 and related pathways. Molecular aspects of medicine, 53, 10–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2016.08.001
- Bird R. P. (2018). The Emerging Role of Vitamin B6 in Inflammation and Carcinogenesis. Advances in food and nutrition research, 83, 151–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2017.11.004
- Mascolo, E., & Vernì, F. (2020). Vitamin B6 and Diabetes: Relationship and Molecular Mechanisms. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(10), 3669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103669
- Nie, C., He, T., Zhang, W., Zhang, G., & Ma, X. (2018). Branched Chain Amino Acids: Beyond Nutrition Metabolism. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(4), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19040954
- Fan, P., Li, L., Rezaei, A., Eslamfam, S., Che, D., & Ma, X. (2015). Metabolites of Dietary Protein and Peptides by Intestinal Microbes and their Impacts on Gut. Current protein & peptide science, 16(7), 646–654. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203716666150630133657

* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
Share
Great Tasting and Doing its Job!
I recently brought back using BCAA’s in my routine supplementation, and I have been feeling great!